JS对象,JSBOM和JSDOM的介绍以及基本运用
一. JavaScript简介
- JavaScript是一种解释性脚本语言(代码不进行预编译),由浏览器解释执行,用来向页面添加交互行为;
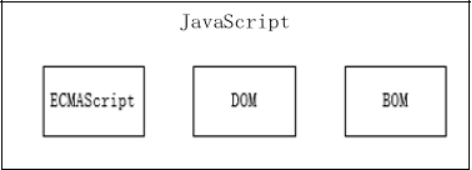
- Java Script由三个主要组成部分:ECMAScript(核心),BOM(浏览器对象模型),DOM(文档对象模型);
- ECMAScript描述了Js的基本语法:类型、语句、关键字、保留字、运算符和对象等。DOM是把整个文档中的所有节点解析成一个一个对象,并且这些对象之间会形成一个层级关系。通过DOM我们可以对文档中所有节点做CRUD操作。BOM是浏览器的一种特性,它可以对浏览器窗口进行访问和操作,例如移动、关闭窗口,调整窗口的大小等;
二. JS三种写法
1.行内JS
1 | <a href="javascript:alert('行内写法')">点我</a> |
2.内部JS
1 | <script type="text/javascript"> |
3.外联JS
1 | <!--js按照顺序执行--> |
三. 数据类型
- js中可以使用typeof 和typeof()判断当前变量属于那种数据类型
1 | var a = true; |
- 无穷数
- 在JS语法中,数字是有取值边界的,超出最大数取值为Infinity【正无穷】,超出最小数取值为-Infinity【负无穷】,无穷数不能用于数值运算,一般使用isFinite()函数对一个数字进行判断是否是有穷的【有限的】,若传入的数据是无穷数,那么返回false,若传入的数据是有穷数,则返回为true;
- 在JS中,1/0并不会报错,因为JS语法中0是取值了一个无限趋近于0的一个数字。
非数
- 不是数字,在JS中采用NAN来表示,同样在JS中采用了isNaN()函数来判定当前字符是否真的不是数字
boolean(布尔类型)
- 在JS语法中,0、NaN、Undefined、空字符串、null均可以表示为false
string(字符串类型)
- JS语法中不存在char类型,所以由单引号或双引号括起来的字符序列,任何字符串的长度都可以通过访问length属性获得
null(空对象)
- 表示一个不存在的对象,只有一个值null
undefined(未定义或未初始化)
- 表示声明但未赋值的对象,Undefined派生自null;
- 如果我们做 -,*、/如果有字符串,它会尝试去转换成number来进行运算,如果转换失败(NaN)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26<script>
//https://w3school.com.cn/
<!--判断是否是无穷数-->
console.log(isFinite(1 / 0));//finite 有限的
let a = 100;
console.log(isNaN(a));//判断是否是一个数字 Not a Number
let b;
console.log(b);//未定义 js的变量值类型是赋值后确定的
let string = "今天是个好日子_咿呀咿呀哟";
//字符串方法
console.log(string.split('_'))//返回字符串数组
// js 中的0,NaN,null,Undefined,空字符串都可以表示位false
console.log("----------------------------------------")
if (!0) {
console.log("值为0:" + 0)
}
if ({}) {
console.log("大括号")
}
if (!NaN) {
console.log("NaN:" + NaN)
}
if (!""){
console.log("空字符串");
}
</script>
四. 运算符
1.关系运算符
比较运算符用于判断两个变量大小关系:>、<、==、<=、>=、===、!=、!==;
(1) == :代表相等(它只比较内容,不比较类型)
(2) ===:绝对相等(先比较类型,再比较内容)
(3) !==:绝对不等
1
2
3
4
5var x = 10;
var y = "10";
console.debug(x==y); //true
console.debug(x===y); //false
console.debug(x!==y); //true
2.逻辑运算符
&& :逻辑AND运算符,一假遍假
|| :逻辑OR运算符 ,一真遍真
! :逻辑NOT运算符,真为假,假为真
1 | <script> |
五.JavaScript流程控制
1 | <script> |
六.JavaScript函数
声明函数的几种方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29<script>
<!-- 无参无返回值 -->
function foo1() {
console.log("我是函数一")
}
//调用函数
foo1();
//有参无返回值
function foo2(a, b) {
console.log(a + b);
}
foo2(39, 1)
//有参有返回值
function foo3(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
console.log(foo3(11, 1));
// 匿名函数
const e = function (a, b) {
return a * b;
};
const e1 = e(1, 1);
console.log(e(11, 11))
</script>
七.JavaScript对象
js的对象有三大类,内部对象(本地对象和内置对象)、宿主对象和自定义对象;
内部对象包括本地对象和内置对象:
(1) 本地对象可以new实例,方法或函数式通过实例调用的;
(2) 内置对象不能使用new关键字创建实例,方法调用也不需要通过实例去调用;
宿主对象指的是BOM和DOM中的所有对象;
自定义对象就是开发人员自己定义的对象。
本地对象Date:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38<script>
let now1 = new Date();
console.log(now1.getFullYear());//获取年份
console.log(now1.getDay());//获取星期
console.log(now1.getMonth() + 1);//获取月份
console.log(now1.getDate());// 返回月中的第几天(从 1 到 31)
console.log(now1.getTime());//返回毫秒数
console.log(now1.toLocaleDateString());//2022/8/8
console.log(now1.toLocaleTimeString());//15:35:20
console.log(now1.constructor);//返回创建 Date 对象原型的函数。
// 自定义日期格式
function format() {
let date = new Date();
let year = date.getFullYear();
let month = date.getMonth() + 1;
let day = date.getDay();
let time = date.toLocaleTimeString();
console.log(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " " + time);
}
format();
//向Date添加方法
Date.prototype.format = function () {
let date = new Date();
let year = date.getFullYear();
let month = date.getMonth() + 1;
let day = date.getDay();
let time = date.toLocaleTimeString();
console.log(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " " + time);
}
//自定义属性
Date.prototype.username = "hello";
let date1 = new Date();
date1.format();
console.log(date1.username);
</script>本地对象String:
1
2
3
4
5
6<script>
let s = "0606,i am a monster, you can call me,哇酷哇酷";
console.log(s.length);//字符串长度
console.log(s.split(','));//分割字符串
console.log(s.substring(5, 19));//截取字符串
</script>内置对象 包括Global、Math这两个
①Global全局对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17<script>
<!-- 编码uri -->
let web = "www.baidu.com?name=春上村树";
console.log(encodeURI(web));//www.baidu.com?name=%E6%98%A5%E4%B8%8A%E6%9D%91%E6%A0%91
//解码
console.log(decodeURI("www.baidu.com?name=%E6%98%A5%E4%B8%8A%E6%9D%91%E6%A0%91"));
/*
eval() 评估字符串并像脚本代码一样执行它。
*/
console.log(eval("12+12"));
// console.log(eval("alert('you are so cute')"));
//解析字符串返回整数 首字符必须位数字 直到找到一个非数字字符返回前面数字字符的整数
console.log(parseInt("1123abc"));
//返回浮点数
console.log(parseFloat("121.2xn"));
</script>②数学计算对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20<script>
<!-- 随机数 -->
console.log(Math.random());//0-1
console.log(Math.cos(180));//余弦
console.log(Math.sign(180));//正弦
const a = 11.11;
const b = -11.11;
//向上取整
console.log(Math.ceil(a));//12
console.log(Math.ceil(b));//-11
//向下取整
console.log(Math.floor(a));//11
console.log(Math.floor(b));//-12
//四舍五入
console.log(Math.round(a));//11
console.log(Math.round(b));//-11
</script>自定义对象三种方式如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66<script>
<!-- 方式一 -->
function User() {
}
User.prototype.name = "coderyeah";
User.prototype.age = 19;
User.prototype.print = function () {
console.log("我的名字是" + this.name + " 今年" + this.age)
}
let user = new User();
console.log(user.name);
user.print()
// 方式二
function Student(name, age, sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.stu = function (name, sex) {
console.log("我是" + name + " 性别:" + sex)
}
}
let stu = new Student("渣渣灰", 22, '男')
console.log(stu.age);
stu.stu("渣渣灰", '男')
// 方式三 常用
let obj = {
name: "栀子花",
price: 99.99,
address: "成都",
color: "white",
intro: function () {
console.log(this.name + " " + this.price + " " + this.address + " " + this.color)
}
}
console.log(obj.name)
obj.intro()
// 一次性定时器
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("hello jack")
}, 1000);
// 周期性定时器
let a = 1;
const timer = setInterval(() => {
// console.log("interval")
if (a == 5) {
window.location.href = "https://www.jd.com/"
clearInterval(timer);//停止定时器任务
}
a++;
console.log(new Date())
}, 1000)
// 地址对象
console.log("location:" + location.href);
// 确认弹框
let bool = confirm("确定要忘记她吗?");
console.log(bool)
</script>
八.BOM
BOM是Browser Object Model的缩写,简称浏览器对象模型;
所有的BOM和DOM中的对象都称之为宿主对象;
BOM的顶级对象是window;
(1) 打开一个窗口就是一个window对象;
(2) 窗口里面使用location表示地址栏;
(3) 窗口的历史记录使用history来表示;
(4) 浏览器的信息使用navigator来表示;
(5) 窗口里面的内容使用document来表示;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19// 周期性定时器
let a = 1;
const timer = setInterval(() => {
// console.log("interval")
if (a == 5) {
//跳转页面
window.location.href = "https://www.jd.com/"
clearInterval(timer);//停止定时器任务
}
a++;
console.log(new Date())
}, 1000)
// 地址对象
console.log("location:" + location.href);
// 确认弹框
let bool = confirm("确定要忘记她吗?");
console.log(bool)
</script>
九.DOM
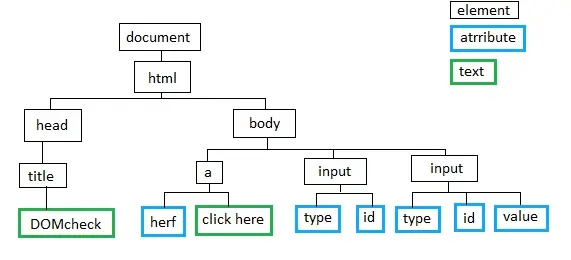
DOM【Document Object Model】 :文档对象模型。直白的讲就是通过程序解析结构化文档(xml,html)的时候,在内存中生成的包含当前结构化文档中所有内容的一个对象模型。文档中的每一个节点都会生成一个对象,这些对象与对象之间会形成一个层级关系,像一个树形结构,所以称之为DOM树;
事件绑定
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17<body>
<!--元素上直接绑定-->
<input type="submit" onclick="show()">
<!--动态绑定方式-->
<button id="btn">保存</button>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
var btn = document.getElementById("btn");
btn.onclick = function () {
alert("保存成功!")
}
}
function show() {
console.log("展示......")
}
</script>
</body>获取节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27<body>
<div id="d1">
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby">读书
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby">看报
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby">睡觉
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby">打豆豆
</div>
<span class="sp">黄金镇魂曲</span>
<span class="sp">性感手枪</span>
<script>
// getElementById("id属性值") -- 常用 // 通过标签元素的ID获取到标签对象 返回HTML集合
const d1 = document.getElementById("d1");
console.log(d1);
// 通过标签名称获取到标签对象,返回的是数组
const input = document.getElementsByTagName("input");
console.log(input);
// getElementsByName() 返回NodeList 通过标签元素的name属性获取到标签对象,返回的是数组
console.log(document.getElementsByName("hobby"));
//通过class值获取到标签对象,返回的是数组
console.log(document.getElementsByClassName("sp"));
// parentNode:父节点,返回Node 获取指定元素的父节点
console.log(d1.parentNode);
console.log(d1.parentElement);
// document.body:获取body节点 <body>
console.log(document.body);
</script>
</body>页面加载事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>页面加载事件</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//页面加载 要等页面加载完成后再执行js代码 因为代码是从上往下开始执行
window.onload = function () {//匿名函数
console.log(document.getElementById("d1"));
}
</script>
<div id="d1">
<h1>i am a monster</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>操作节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22<div id="d1">
<input type="number" name="age" value="22" style="color: green; font-size: 26px">
<span id="s">我系乔巴纳</span>
</div>
<script>
//获取节点
const d1 = document.getElementById("d1");
//创建节点
const inp = document.createElement("input");
//添加节点属性
inp.type = "text";
inp.name = "username";
inp.value = "吉良吉影";
inp.style.color = "red";
inp.style.fontSize = "28px";
//添加节点
d1.appendChild(inp)
// 删除节点 通过获取父节点进行删除
const s = document.getElementById("s");
// d1.removeChild(s)
console.log(s.parentElement.removeChild(s));//<span id="s">我系乔巴纳</span>
</script>操作属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27<div id="d1">
<input id="inp1" name="username">
</div>
<script>
var d1 = document.getElementById("d1");
var inp1 = document.getElementById("inp1");
//获取属性 方式一
console.log(inp1.getAttribute("name"));
console.log(inp1.getAttribute("id"));
//获取属性 方式二
console.log(inp1.id);
console.log(inp1.name);
//添加属性方式一
// inp1.setAttribute("value", "空条徐伦")
//添加属性方式二
// inp1.value="哈哈哈哈哈"
inp1.value = "啊啊啊啊啊";
inp1.style.color = "red";
inp1.style.fontSize = "25px";
//删除属性
inp1.removeAttribute("value")
inp1.removeAttribute("name")
//赋空值
inp1.value = "";
</script>操作样式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>操作样式</title>
<style>
.myClass {
background-color: skyblue;
font-size: 26px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input id="in" type="text" name="name" value="root">
<script type="text/javascript">
const inp = document.getElementById("in");
inp.style.color = "red"
inp.className="myClass";
</script>
</body>
</html>操作文本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17<ul id="ul">
<li>《老友记》</li>
<li>《平凡的世界》</li>
<li>《左手倒影,右手年华》</li>
<li>《天才在左,疯子在右》</li>
</ul>
<script type="text/javascript">
var ul = document.getElementById("ul");
//innerHTML 获取标签+文本内容
console.log(ul.innerHTML);
//innerText 获取文本内容
console.log(ul.innerText);
//重新赋值 如果直接赋值会覆盖所有
ul.innerHTML = ul.innerHTML + "<li>《倒影》</li>"
//赋值文本
// ul.innerText = ul.innerText + "《倒影》"
</script>鼠标事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16<div id="d1" style="width: 300px;height: 300px;background-color: pink">
</div>
<script>
//加载事件
window.onload = function () {
var d1 = document.getElementById("d1");
//鼠标移入事件
d1.onmouseover = function () {
d1.innerHTML = "<span style='background-color: wheat'>我移动上来了哦</span>";
}
//鼠标移出事件
d1.onmouseout = function () {
d1.innerText = "我出去了啊";
}
}
</script>焦点事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15<input type="text" id="inp">
<script>
//页面加载事件
window.onload = function () {
var inp = document.getElementById("inp");
inp.onfocus = function () {
//获取焦点
console.log('得到了')
}
//失去焦点
inp.onblur = function () {
console.log("我还是失去了你......")
}
}
</script>综合案例—-打地鼠
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>打地鼠</title>
<style>
.dishu {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid black;
border-radius: 50%; /* 圆角 */
position: absolute; /* 定位 */
/*
要随机出现在不同的位置,所以位置不能写死
top:100px;
left:200px;
*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body style="background-color: skyblue">
<script>
//加载页面事件
window.onload = function () {
//设置周期性定时器
setInterval(() => {
//1.创建img标签
const img = document.createElement("img");
//2.为img标签设置属性
img.src = "./static/img/1.jpg";
img.className = "dishu";
//3.获取画布(body)宽高 减去图片的宽高是为了解决图片显示不完整bug
const width = document.documentElement.clientWidth - 100;
const height = document.documentElement.clientHeight - 100;
//随机数范围是 0~1 这里设置的是X,Y坐标 边界距离
const left = Math.random() * width + "px";
const top = Math.random() * height + "px";
img.style.left = left;
img.style.top = top;
//添加img标签到父标签
document.body.appendChild(img);
//4.设置图片的点击事件
img.onclick = function () {
//点击之后删除当前标签
this.parentNode.removeChild(this);
}
}, 2000);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
十. Ajax:异步请求,局部刷新
优点:
- 异步请求,发送请求的同时还可以继续操作页面。页面不销毁;
- 返回部分数据,减少不必要的数据传输,减少网络资源。页面不刷新,而是更新页面部分数据。
Ajax实质:通过浏览器得到一个ajax对象,再通过ajax对象发送请求。
同步和异步:
同步:你先做完我再做(排队),后一步的操作必须要等待前一步操作的结果;
异步:各做各的相互不干扰(效率高,但安全性较低)。
Ajax发送请求的步骤
①获取ajax对象;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7//获取ajax对象
var xhr = null;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {//针对其他浏览器
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {//针对低版本的ie浏览器
xhr = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP');
}②准备发送请求:xhr.open(“post”,”/xx/add”)
1
2
3
4//创建请求
xhr.open("post", "/req");
//设置请求头, application/x-www-form-urlencoded表示请求的参数是字符串格式
xhr.setRequestHeader("content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");③设置回调函数(主要是获取服务器返回的正确数据):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8//回调函数
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState == 4 && xhr.status == 200) {//已经接收到服务器响应的内容了
var txt = xhr.responseText;
//展示数据到页面
document.getElementById("msg").innerText = txt;
}//这里最后不要写else,因为状态从0-1-2-3都会触发else
};④发送请求
1
2//发送请求 这里采用post方式发送请求,请求参数就不能拼接在请求路径后面
xhr.send("username=" + document.getElementById("username").value);