分布式事务的实现方案和redis缓存配置
一.什么是分布式事务
针对于单数据库的事务我们叫着本地事务/传统事务,在分布式环境中一个请求可能涉及到多个数据库的写操作(多数据源),要保证多数据源的一致性必须用到分布式事务。
二.为什么需要分布式事务
系统微服务化后,一个看似简单的功能,内部可能需要调用多个服务并操作多个数据库实现,服务调用的分布式事务问题变的非常突出。
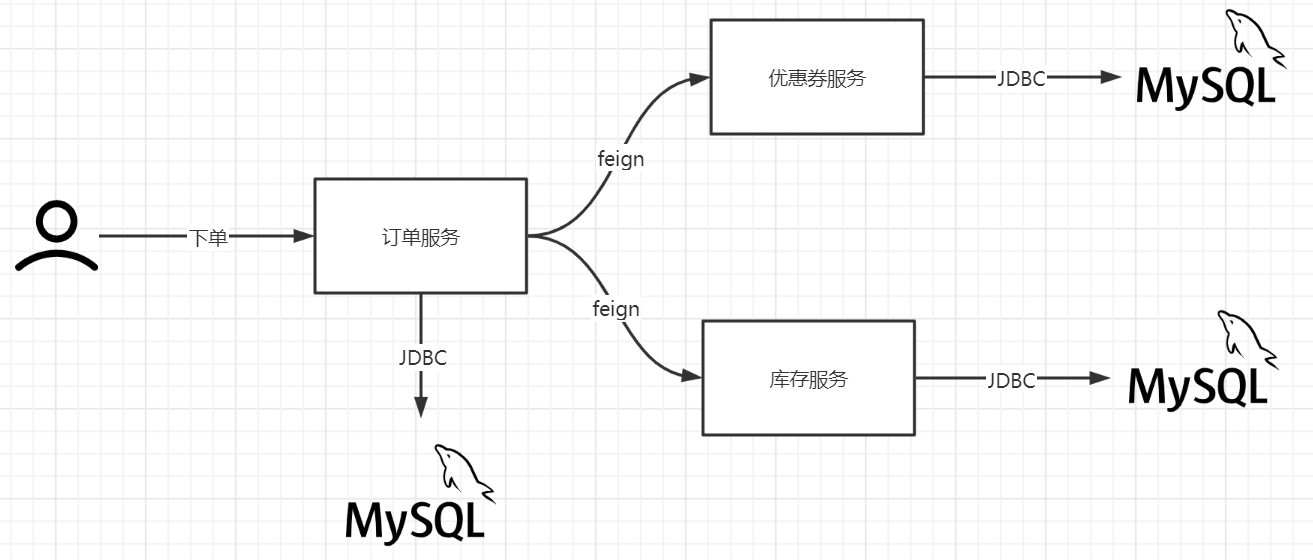
一个下单请求同时设计到订单库,优惠券库,库存库的写操作,需要保证三个库写操作的一致性,就要用到分布式事务 即:分布式事务就是要解决一个请求同时对多个数据库写操作的一致性
注意:微服务拆分原则,尽量让大部分操作都不要跨微服务操作,也就是跨库。 分布式事务比本地事务耗费的资源更多。
三.分布式事务解决方案
2PC方案
2PC即两阶段提交协议,是将整个事务流程分为两个阶段,准备阶段( Prepare phase).提交阶段( pphase ) , 2是指两个阶段, P是指准备阶段, C是指提交阶段。
在第一阶段(准备阶段),事务管理器先事务参与者(资源)们发送准备请求,大家都返回OK状态,那么就进入第二阶段,提交事务,如果在第一阶段有任何一个参与者没有OK,那么事务协调器通知其他所有事务参与者(资源)回滚事务。2PC常见的标准是XA, JTA,Seata等。
基于Seata的2pc
Seata是由
阿里中间件团队发起的开源项目Fescar ,后更名为Seata ,它是一个是开源的分布式事务框架。传统2PC的问题在Seata中得到了解决,它通过对本地关系数据库的分支事务的协调来驱动完成全局事务,是工作在应用层的中间件。主要优点是性能较好,且不长时间占用连接资源,它以高效并且对业务0侵入的方式解决微服务场景下面临的分布式事务问题,它目前提供AT模式(即2PC)及TCC模式的分布式事务解决方案。- Transaction Coordinator(TC):事务协调器,它是独立的中间件,需要独立部署运行,它维护全局事务的运行状态,接收TM指令发起全局事务的提交与回滚,负责与RM通信协调各各分支事务的提交或回滚。 相当于是一个软件需要单独部署
- Transaction Manager (TM):事务管理器, TM需要嵌入应用程序中工作,它负责开启一个全局事务,并最终 向TC发起全局提交或全局回滚的指令。
- Resource Manager (RM):资源管理器控制分支事务, 负责分支注册、状态汇报,并接收事务协调器TC的指令, 驱动 分支(本地)事务的提交和回滚。
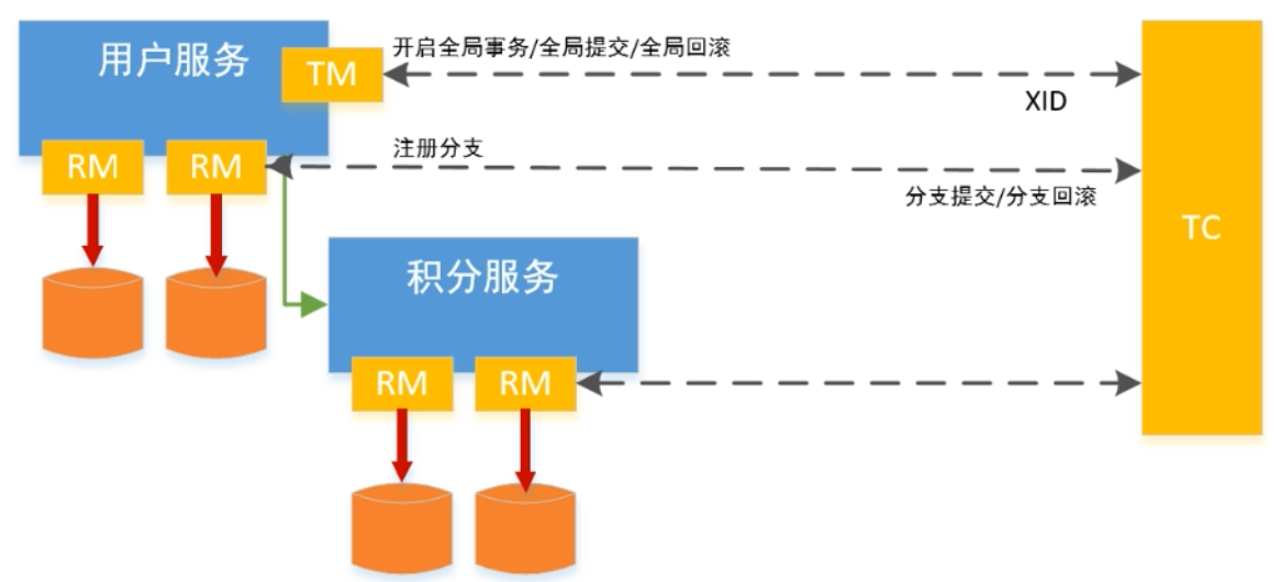
事务流程如下
具体的执行流程如下:
- 用户服务的TM向TC申请开启一个全局事务,全局事务创建成功并生成一个全局唯一的XID。
- 用户服务的RM向TC注册分支事务,该分支事务在用户服务执行新增用户逻辑,并将其纳入XID对应全局事务的管辖。
- 用户服务执行分支事务,向用户表插入一条记录。
- 逻辑执行到远程调用积分服务时(XID在微服务调用链路的,上下文中传播)。积分服务的RM向TC注册分支事务,该分支事务执行增加积分的逻辑,并将其纳入XID对应全局事务的管辖。
- 积分服务执行分支事务,向积分记录表插入一条记录,执行完毕后,返回用户服务。
Seata 分布式事务:https://blog.csdn.net/u014494148/article/details/105781920
四.注册集成Seata
1.下载
- 下载:https://github.com/seata/seata/tags
- 启动:seata-server.bat -p 8091 -h 127.0.0.1 -m file
导入依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.9</version>
</dependency>yml配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7seata:
enableAutoDataSourceProxy: false #关闭DataSource代理的自动配置,我们要手动配置
spring:
cloud:
alibaba:
seata:
tx-service-group: fsp_tx_group #这里和file.conf中事务组名一样拷贝配置
1.resources/file.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66transport {
tcp udt unix-domain-socket
type = "TCP"
NIO NATIVE
server = "NIO"
enable heartbeat
heartbeat = true
the client batch send request enable
enableClientBatchSendRequest = true
thread factory for netty
threadFactory {
bossThreadPrefix = "NettyBoss"
workerThreadPrefix = "NettyServerNIOWorker"
serverExecutorThread-prefix = "NettyServerBizHandler"
shareBossWorker = false
clientSelectorThreadPrefix = "NettyClientSelector"
clientSelectorThreadSize = 1
clientWorkerThreadPrefix = "NettyClientWorkerThread"
# netty boss thread size,will not be used for UDT
bossThreadSize = 1
#auto default pin or 8
workerThreadSize = "default"
}
shutdown {
# when destroy server, wait seconds
wait = 3
}
serialization = "seata"
compressor = "none"
}
service {
transaction service group mapping
vgroupMapping.fsp_tx_group = "default"
only support when registry.type=file, please don't set multiple addresses
default.grouplist = "127.0.0.1:8091"
degrade, current not support
enableDegrade = false
disable seata
disableGlobalTransaction = false
}
client {
rm {
asyncCommitBufferLimit = 10000
lock {
retryInterval = 10
retryTimes = 30
retryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict = true
}
reportRetryCount = 5
tableMetaCheckEnable = false
reportSuccessEnable = false
}
tm {
commitRetryCount = 5
rollbackRetryCount = 5
}
undo {
dataValidation = true
logSerialization = "jackson"
logTable = "undo_log"
}
log {
exceptionRate = 100
}
}2.resources/registry.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83registry {
# file 、nacos 、eureka、redis、zk、consul、etcd3、sofa
type = "file"
nacos {
serverAddr = "localhost"
namespace = ""
cluster = "default"
}
eureka {
serviceUrl = "http://localhost:8761/eureka"
application = "default"
weight = "1"
}
redis {
serverAddr = "localhost:6379"
db = "0"
password = ""
cluster = "default"
timeout = "0"
}
zk {
cluster = "default"
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:2181"
session.timeout = 6000
connect.timeout = 2000
username = ""
password = ""
}
consul {
cluster = "default"
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8500"
}
etcd3 {
cluster = "default"
serverAddr = "http://localhost:2379"
}
sofa {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:9603"
application = "default"
region = "DEFAULT_ZONE"
datacenter = "DefaultDataCenter"
cluster = "default"
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
addressWaitTime = "3000"
}
file {
name = "file.conf"
}
}
config {
# file、nacos 、apollo、zk、consul、etcd3、springCloudConfig
type = "file"
nacos {
serverAddr = "localhost"
namespace = ""
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
}
consul {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8500"
}
apollo {
app.id = "seata-server"
apollo.meta = "http://192.168.1.204:8801"
namespace = "application"
}
zk {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:2181"
session.timeout = 6000
connect.timeout = 2000
username = ""
password = ""
}
etcd3 {
serverAddr = "http://localhost:2379"
}
file {
name = "file.conf"
}
}排除DataSource自动配置
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
.MybatisPlus版本
把DataSource交给Seata代理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50package io.coderyeah.ymcc.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean;
import io.seata.rm.datasource.DataSourceProxy;
import org.mybatis.spring.transaction.SpringManagedTransactionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* 数据源代理
*/
public class DataSourceConfiguration {
//mapper.xml路径
private String mapperLocations;
//手动配置bean
public DataSource druidDataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
public MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy) throws Exception {
//处理MybatisPlus
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSourceProxy);
factory.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(mapperLocations));
//事务管理工厂
factory.setTransactionFactory(new SpringManagedTransactionFactory());
return factory;
}
public DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy(DataSource druidDataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(druidDataSource);
}
}Mybatis版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import io.seata.rm.datasource.DataSourceProxy;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.transaction.SpringManagedTransactionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
//使用seata对DataSource进行代理
public class DataSourceProxyConfig {
//mapper.xml路径
private String mapperLocations;
//手动配置bean
public DataSource druidDataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
public SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSourceProxy);
sessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(mapperLocations));
//事务管理工厂
sessionFactoryBean.setTransactionFactory(new SpringManagedTransactionFactory());
return sessionFactoryBean.getObject();
}
public DataSourceProxy dataSource() {
return new DataSourceProxy(druidDataSource());
}
}业务方法
方法上贴 : @GlobalTransactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) 开启Seata全局事务
2.6.注释事务开启注解
注意:不能加@EnableTransactionManagement 注解了 , 也不需要加@Transactional
2.7.undolog表
数据库中创建表,涉及到事务的表都需要添加undolog
1 | -- 注意此处0.3.0+ 增加唯一索引 ux_undo_log |
五.redis分布式缓存
导入依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
<version>2.10.0</version>
</dependency>yml配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13spring:
application:
name: service-user #服务名
redis:
host: 43.136.61.70
port: 6379
password: 123456
database: 0
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 8
max-idle: 8
max-wait: 2000msRedis序列化配置
我们通常以JSON格式将数据存储到Redis中,这种格式是所有编程语言通用的,所以我们可以把Redis的序列化方式配置为JSON ,这样的话我们就可以不用自己去转JSON了.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26//缓存的配置
public class RedisConfig {
private RedisConnectionFactory factory;
//使用JSON进行序列化
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//JSON格式序列化
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();
//key的序列化
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value的序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//hash结构key的虚拟化
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
//hash结构value的虚拟化
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
}举例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12List<CourseType> list = null;
final Object o = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(YmccConstants.CACHE_COURSE_TYPE);
if (null != o) {
// 从redis中读取返回数据
list = (List<CourseType>) o;
System.out.println("-------redis");
} else {
list = getCourseTypes();
// 存入redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(YmccConstants.CACHE_COURSE_TYPE, list);
System.out.println("-------mysql");
}
六.SpringCache缓存
SpringCahce对缓存流程进行了简化封装,提供了一些注解,我们通过简单的打注解就能实现缓存的添加,修改,删除等,注解如下:
@Cacheable:触发缓存写入。
@CacheEvict:触发缓存清除。
@CachePut:更新缓存(不会影响到方法的运行)。
@Caching:重新组合要应用于方法的多个缓存操作。
@CacheConfig:设置类级别上共享的一些常见缓存设置。
配置SpringCache
继承 CachingConfigurerSupport 对SpringCache进行配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64package io.coderyeah.ymcc.config;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
public class CacheConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
private RedisConnectionFactory factory;
/*
* 自定义生成redis-key , 类名.方法名
*/
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return (o, method, objects) -> {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(o.getClass().getName()).append(".");
sb.append(method.getName()).append(".");
for (Object obj : objects) {
sb.append(obj.toString());
}
System.out.println("keyGenerator=" + sb.toString());
return sb.toString();
};
}
public CacheResolver cacheResolver() {
return new SimpleCacheResolver(cacheManager());
}
public CacheErrorHandler errorHandler() {
// 用于捕获从Cache中进行CRUD时的异常的回调处理器。
return new SimpleCacheErrorHandler();
}
//缓存管理器
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.disableCachingNullValues() //不允许空值
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
//值使用JSON序列化
.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory).cacheDefaults(cacheConfiguration).build();
}
}开启SpringCache
在启动类注解:@EnableCaching
【
特别注意】缓存注解不能加在内部方法上,比如:方法A调用方法B,给方法B加上缓存注解会失效,因为内部方法调用代理会失效。在A方法上打注解即可。
添加缓存
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
public List<CourseType> treeData() {
/* List<CourseType> list = null;
final Object o = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(YmccConstants.CACHE_COURSE_TYPE);
if (null != o) {
// 从redis中读取返回数据
list = (List<CourseType>) o;
System.out.println("-------redis");
} else {
list = getCourseTypes();
// 存入redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(YmccConstants.CACHE_COURSE_TYPE, list);
System.out.println("-------mysql");
}*/
log.debug("=============查询了数据库============");
return getCourseTypes();
}
// 从数据库中查询
private List<CourseType> getCourseTypes() {
// 查询所有分类
List<CourseType> courseTypes = selectList(null);
// 将集合转换为map
Map<Long, CourseType> map = courseTypes.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(CourseType::getId, courseType -> courseType));
// 返回给前端的集合
List<CourseType> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历
courseTypes.forEach(courseType -> {
if (courseType.getPid() == null || courseType.getPid() == 0) {
// 顶级
list.add(courseType);
} else {
// 找到父级
CourseType type = map.get(courseType.getPid());
if (type != null) {
type.getChildren().add(courseType);
}
}
});
return list;
}剔除缓存
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18// 剔除缓存
public boolean insert(CourseType entity) {
return super.insert(entity);
}
public boolean deleteById(Serializable id) {
return super.deleteById(id);
}
public boolean updateById(CourseType entity) {
return super.updateById(entity);
}